Bitcoin ETF - a complete breakdown of what it is, why you might need it and its returns over 3M, 6M and 3Y

What is an ETF?
ETF stands for exchange-traded fund. It's an asset that can be freely bought or sold on the stock market, just like shares of Apple or Tesla.
An ETF works quite similarly to a company's stock. The difference is that instead of representing a stake in a business, an ETF share represents a stake in a fund that holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or, in this case, cryptocurrencies.
A Bitcoin ETF follows the same model and lets you profit from changes in the Bitcoin price without buying the actual coin on a crypto exchange. You simply buy a share of the fund through your regular brokerage account.
Technical aspects of storing bitcoin - crypto wallets, Bitcoin addresses and private keys-intimidate newcomers and put some investors off. An ETF removes that friction and makes entry simple and familiar.
Below you will learn about the drawbacks and advantages of ETFs, how they function and why they matter for the crypto market.
How much can an ETF deliver?
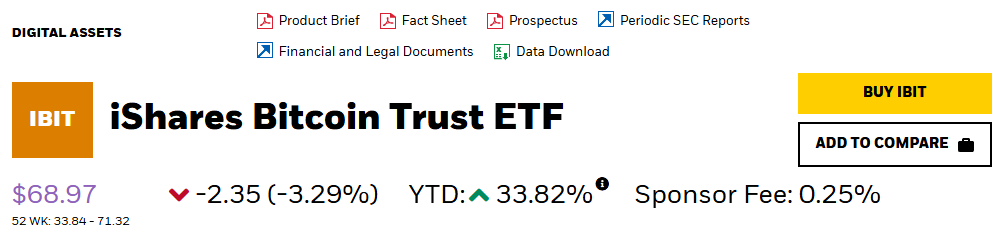
BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF (IBIT) became the most profitable exchange-traded fund by assets under management, outperforming products that had been generating returns for more than two decades.
The fund delivered 33.82 % annualized.
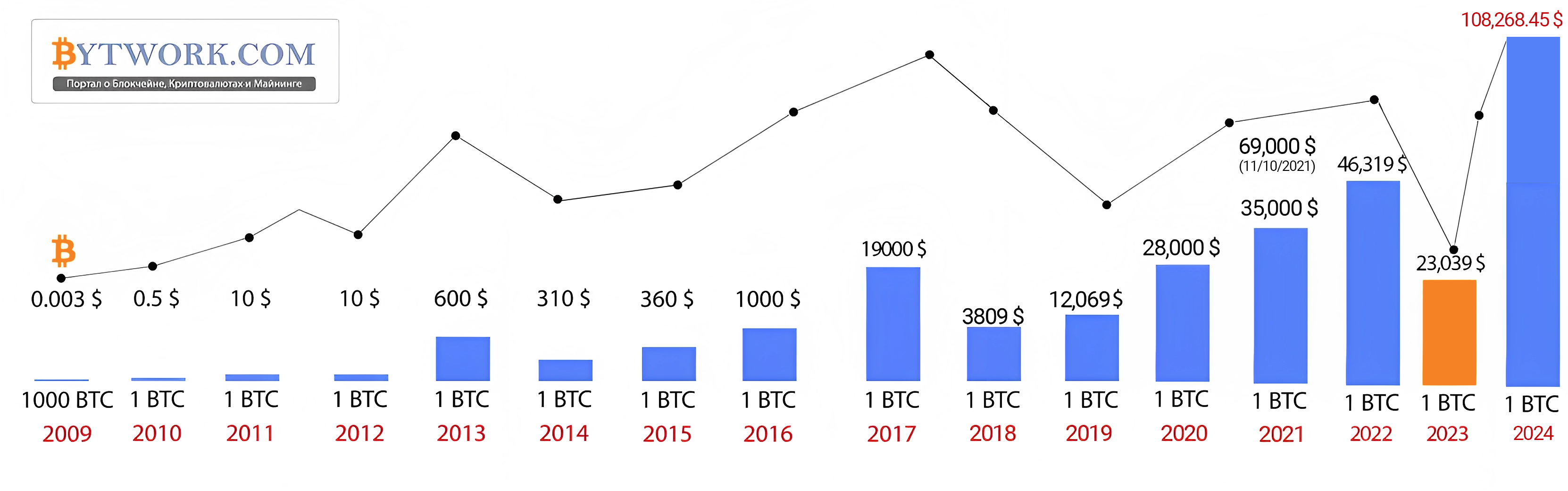
That is respectable, yet Bitcoin’s price history shows the asset is capable of moves far larger, for example 1 000 %. Study the price chart and Bitcoin’s origin story to understand how the network behaves.
You can also read an analysis of Bitcoin cycles to learn how to “catch the tail” of the next move.
Regional rules matter too.
- In the United States you can buy Bitcoin ETFs that track the spot price (BlackRock, Fidelity and others).
- In Europe regulatory limits keep spot Bitcoin ETFs off the market, so investors use Bitcoin ETNs-debt instruments backed by the asset.
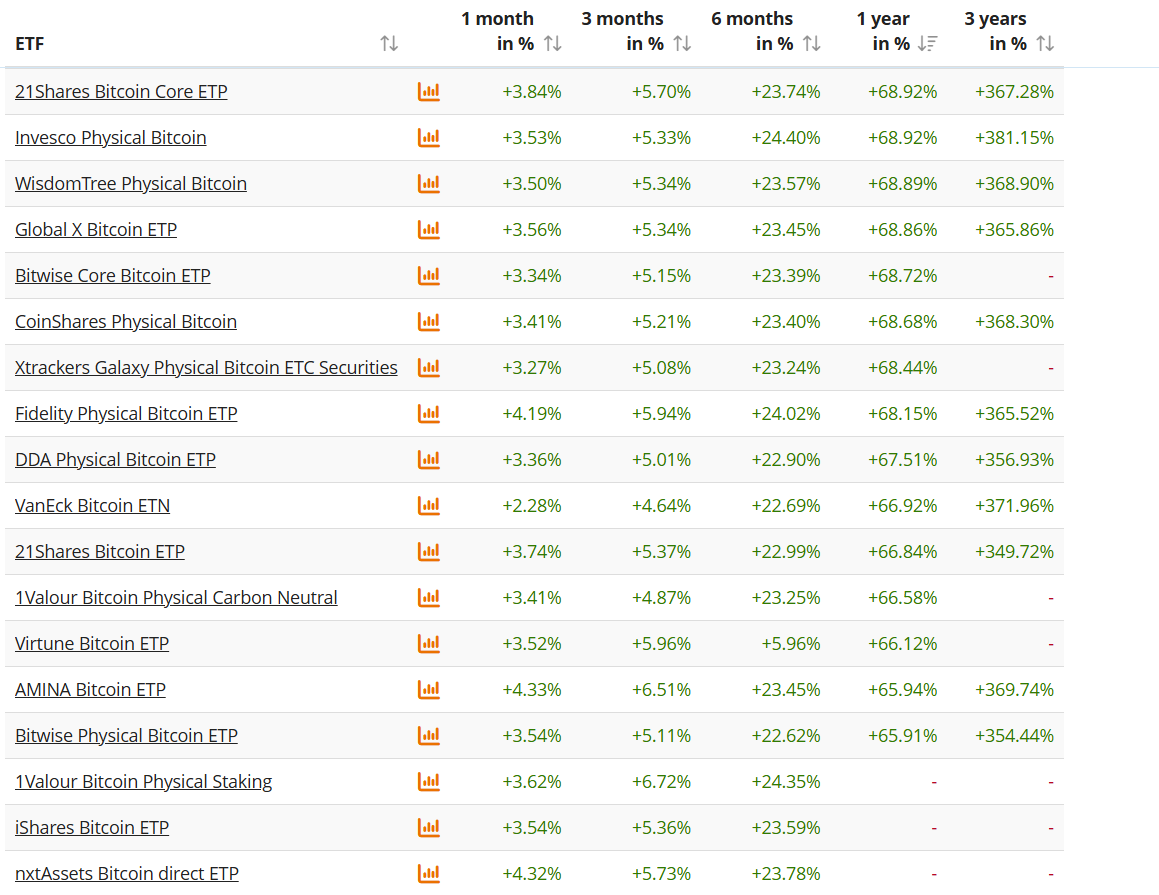
According to JustETF, returns vary across products.
Despite short-term noise, every listed ETP has posted exceptional long-term performance.
Below you can check the live market chart.
Why does a Bitcoin ETF exist?
So why don’t investors just buy Bitcoin directly? A Bitcoin ETF removes the learning curve of wallets, security and custody, giving everyday investors seamless exposure through traditional brokerage accounts.
Advantages
- Regulation. Oversight by financial authorities lowers counter-party risk.
- Beginner friendly. Buying shares feels identical to buying Apple or Nike; no need to master seed phrases or on-chain fees.
- Fund bears the risk. If the custodian is hacked, the legal entity-not you-must make investors whole.
Yet the wrapper has its own costs.
Drawbacks
If you do not purchase the asset itself, technically you do not own it. As the saying goes, not your keys, not your coins. In an ETF the underlying bitcoin belongs to the fund, not to you.
Other ETF disadvantages include
- High fund fees - you pay intermediaries for convenience.
- Closure risk - an unpopular fund can be liquidated.
- No DeFi utility - you cannot stake, lend or otherwise deploy the coins in DeFi.
-
The ETF may not track Bitcoin’s price perfectly because of liquidity gaps, roll costs or timing mismatches.
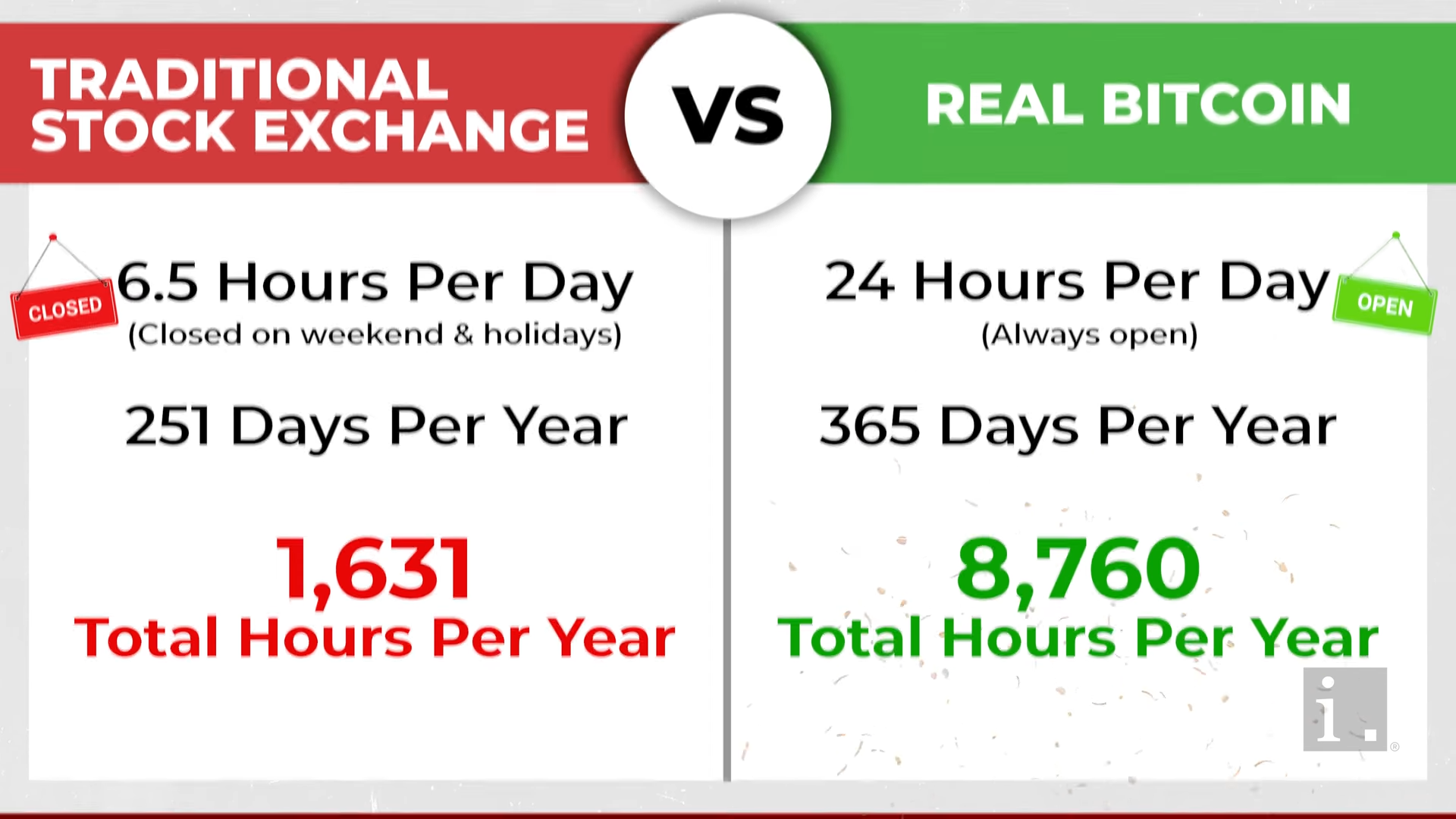
- Trading hours are shorter than the 24/7 crypto market, a pain for active traders.
Choosing between real Bitcoin and a Bitcoin ETF comes down to how much control you want and how you plan to use the asset. Research both paths before you decide.
How does a Bitcoin ETF work?
A firm creates the ETF, buys actual Bitcoin, stores it with a custodian and lists the shares on a traditional stock exchange. You trade those shares exactly like any other stock.
The fund can hold physical bitcoin or derivatives linked to its price, giving rise to two types-spot and futures ETFs.
What is a spot ETF?
A spot ETF means every share is backed by real bitcoin sitting on the blockchain. Large market participants create new shares by delivering the underlying coins, generating genuine demand.
What is a futures ETF?
A futures ETF holds contracts that bet on the future price of Bitcoin rather than the asset itself. This can produce higher volatility and deviation from spot prices.
Bitcoin ETFs also open new trading tactics such as short selling, letting investors bet against the price of Bitcoin.
How are crypto ETFs different from traditional ones?
Key distinctions exist between Bitcoin ETFs and conventional equity ETFs.
First, some ETFs that track the S&P 500 hold dividend-paying stocks. When Tesla pays a dividend, ETF shareholders receive a slice. Bitcoin is decentralised and pays no dividends, so a Bitcoin ETF will not either.
Second, like any ETF you pay an expense ratio, but with a Bitcoin ETF part of that fee covers the custody and security of the underlying coins.
Why are ETFs important for the market?
The launch of a Bitcoin ETF can act as a catalyst for mass adoption, channeling institutional capital-from pension funds to university endowments-into the space.
More buyers mean more demand, and more demand pushes the Bitcoin price higher.
This is not financial advice. The article on Bytwork is for informational purposes only.