Reasons for high fees in Electrum and ways to reduce them
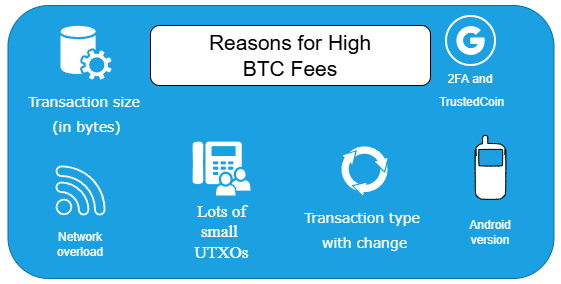
Electrum users often face high fees, even when the network is not congested. Fees can reach high values (30+ satoshi per byte). This depends on the size of the transaction, its type, the addresses used, and the number of unspent transactions (UTXO).
Understand Electrum from scratch: set up a wallet, protect your bitcoins, and learn how to save on transactions.
This article explains the main reasons for high Bitcoin fees and how to reduce them. So, the reasons:
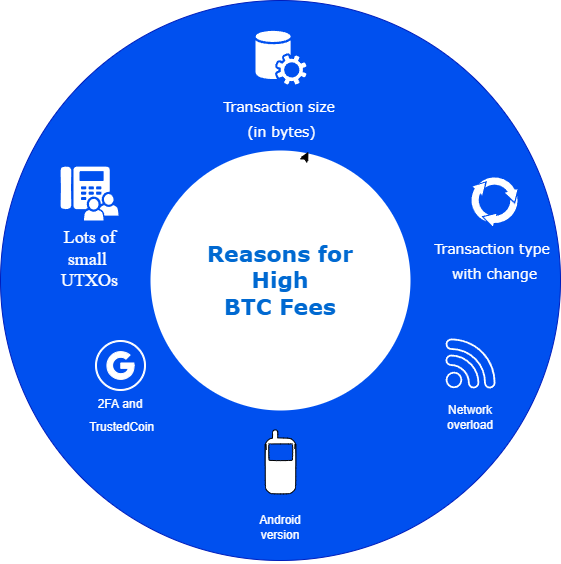
Key Factors Behind High Bitcoin Fees
Transaction size (in bytes)
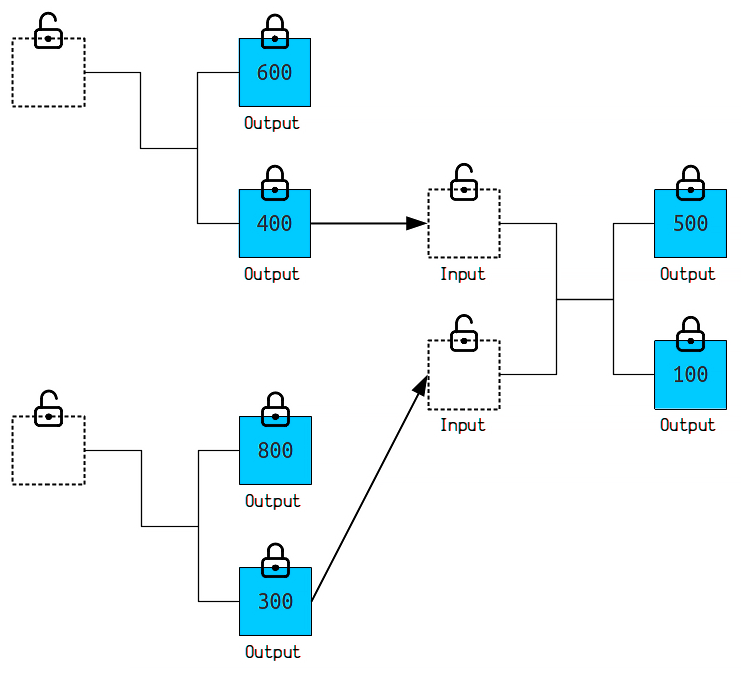
The fee is based on the size of the transaction in bytes, not the amount transferred. A transaction consists of inputs (the sources of bitcoins) and outputs (the destination addresses). Each input and output adds data to the payment structure. The more of these elements, the larger the transaction size and, accordingly, its cost to include in a block.
Transaction inputs and outputs
Lots of small UTXOs
A lot of small unspent transaction outputs, called UTXOs, accumulate in the wallet. This can cause high fees due to the increased transfer size.
A separate processing fee is calculated for each small amount.
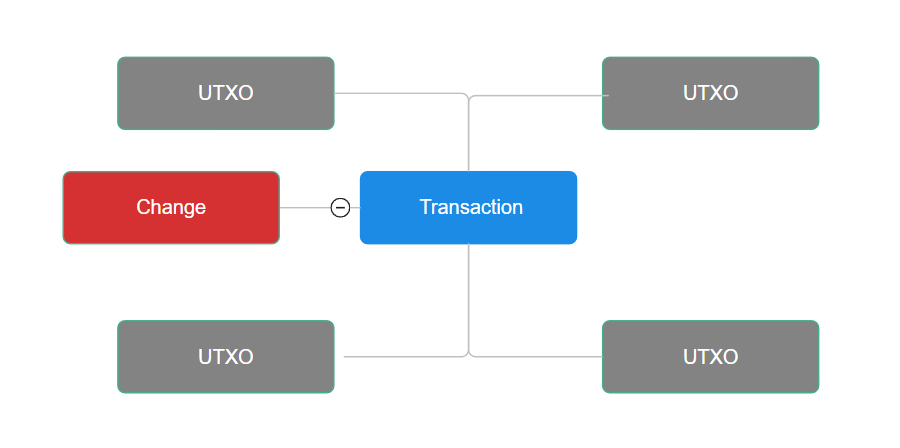
Transactions involving change outputs
If a transaction includes change, it also increases its size. This happens if the sender's address has more bitcoins than were required for the transfer.
Change is a transaction with unspent payments that appear due to the peculiarities of the blockchain and the UTXO system.
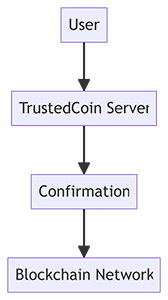
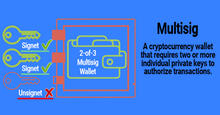
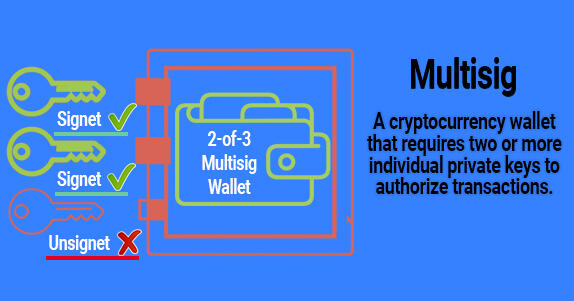
2FA and TrustedCoin
TrustedCoin is a partner company of Electrum. It charges a fee for providing 2FA with multi-signature (2 of 3 keys). TrustedCoin server securely stores one of the keys and signs transactions after confirmation via one-time password (OTP).
The price of the additional fee increases if you have enabled two-factor authentication (2FA) with signing transactions via TrustedCoin.
The fee can be high, as it includes the costs of protecting the infrastructure, maintaining servers, and supporting users. But it is limited: no more than 0.5 mBTC (50,000 satoshi) per transaction and a maximum of 20 mBTC (2,000,000 satoshi) for prepayment.
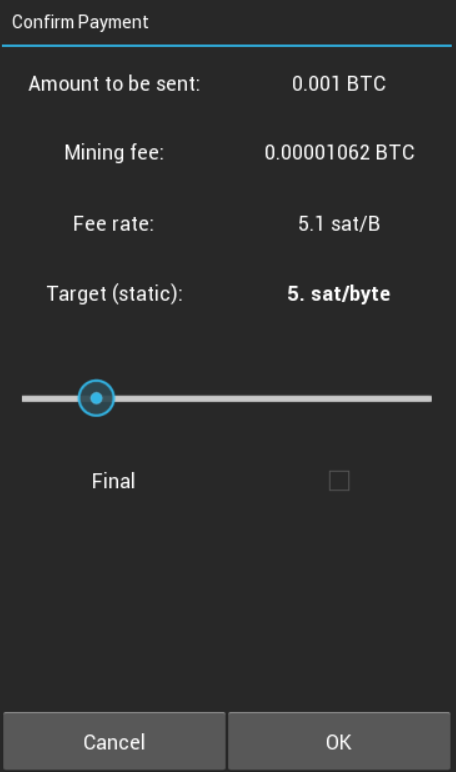
Android version
Although the Android version has an improved interface and new features, the ability to manually set the fees is still missing. There is only a slider with pre-set commissions (1, 2, 5, 10, 20 sat/vB).
Network congestion
If the network is overloaded, the fee will automatically increase to ensure that the transaction is processed faster. However, even at low load, the network may have high fees if you have not configured your wallet properly.
More transactions → higher fees.
How to reduce fees
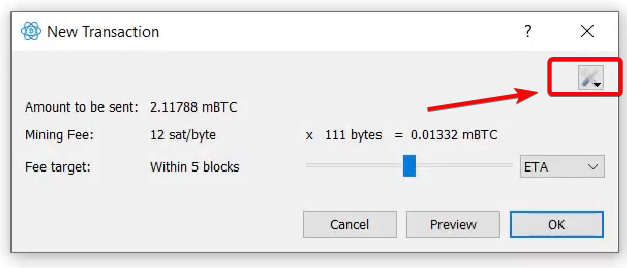
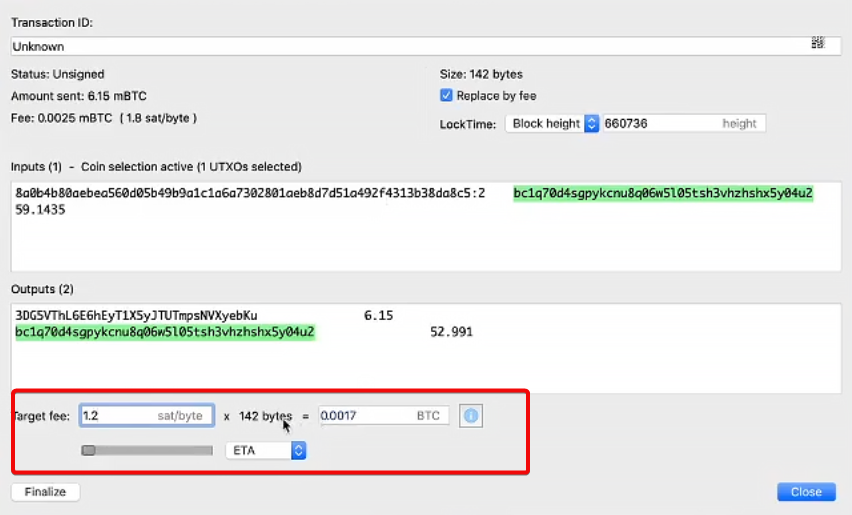
When creating a transaction, you are given a choice: either a slider with a change in commission, or advanced settings.
Click the Advanced icon to set up custom settings.
Specify the size of Sat/vbytes using fee calculator
In the Fee target field, specify the fee in sat/vbyte (satoshi per byte) or select a fixed amount in BTC.
How is the commission calculated
The fee depends on the transaction size in vbyte (virtual bytes). The more data in the transaction, the higher its size and the fee.
A transaction consists of inputs and outputs:
- Inputs are the bitcoins you have received from previous transactions.
- Outputs are the bitcoins you send to another user.
For example :
- A transaction with 1 input and 1 output takes 109.5 vbytes.
- A transaction with 2 inputs and 1 output is 177.25 vbytes.
Since the blockchain “remembers everything,” each input links the current transaction to the history of previous ones, which increases its size and, accordingly, the commission.
Use the Bitcoinfees calculator. The site shows the fee as sat/vB.
Recommendations for reducing commission
- For fast confirmation under high network load, set 20–30
sat/vbyte. - In quiet periods, 10–12
sat/vbyteis sufficient. - To reduce the fee if there is no urgency, select 5–7
sat/vbyte.
Is it possible to set a minimum commission?
Author's experience:
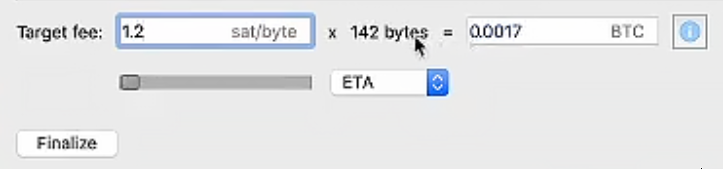
"Enter a little more than the minimum value (for example, 1.2 sat/byte), because many people enter the very minimum - 1 sat/byte. This speeds up confirmation, but does not increase costs."
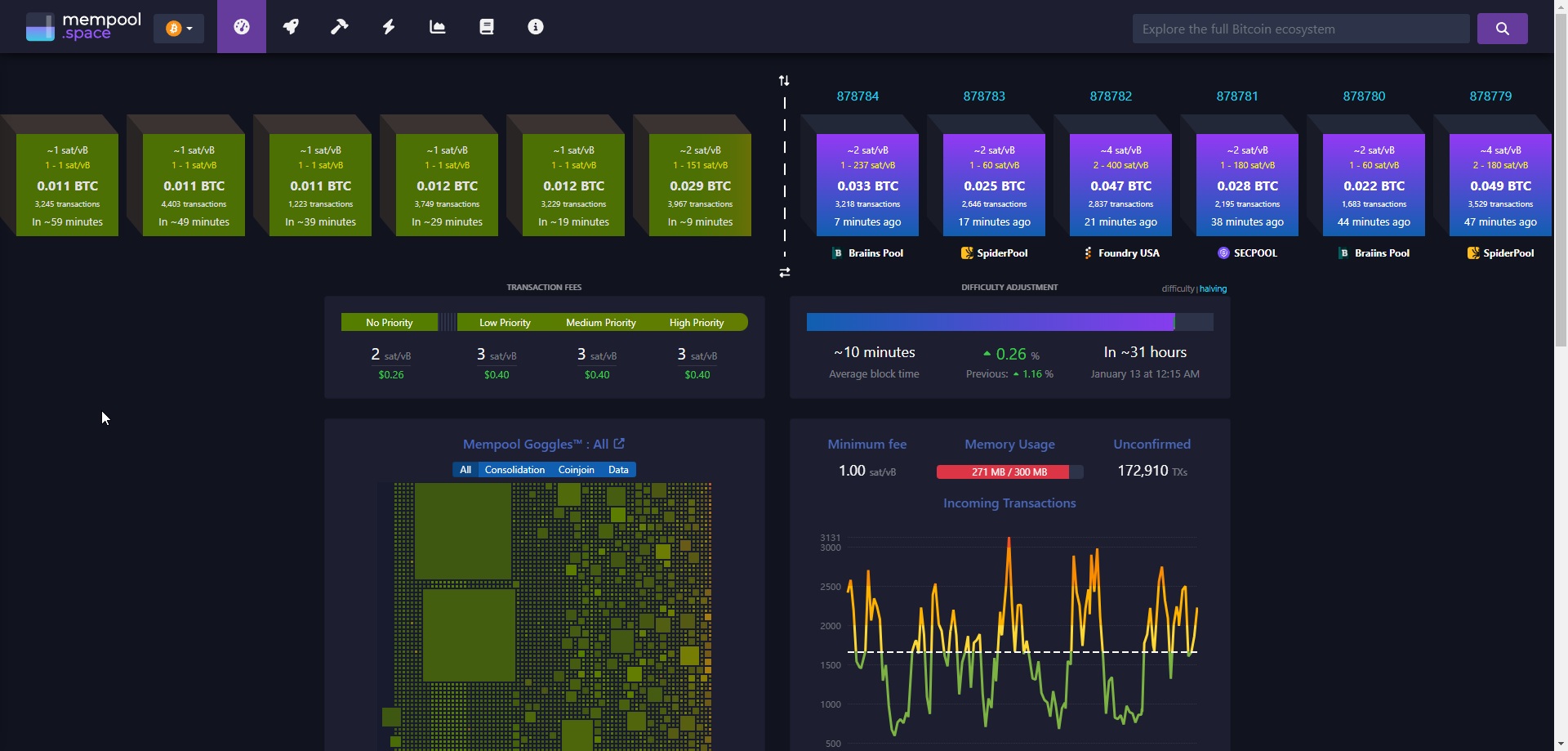
Too low a fee can cause payments to hang. To avoid delays, it is important to monitor the state of the transaction queue - the mempool.
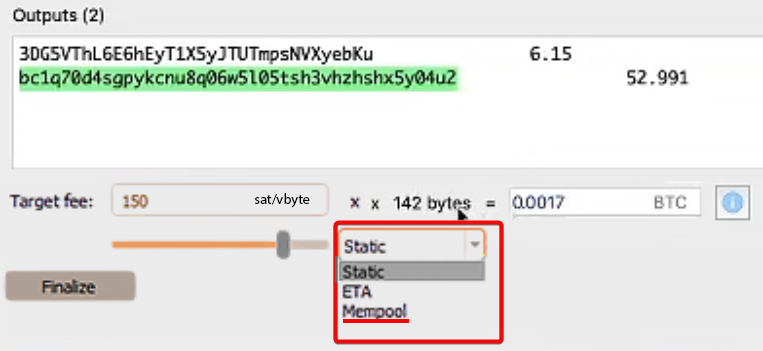
Mempool, ETA and Static – choosing the type of fee
Mempool is one of 3 commission options:
Mempool- provides a forecast based on the current state of the transaction queue. This is the most cost-effective option. However, the more unconfirmed transactions, the higher the fee for priority confirmation.ETA- commission rate for confirmation time (10 or 30 minutes). Automatically selects values taking into account network load. This is the default value.Static- completely manual commission settings. Requires experience And observations for mempool.
When choosing a static commission (Static), its fixed size does not take into account the network load, which can lead to unnecessary expenses. It is better to use the Mempool setting or move the commission slider depending on the actual network load.
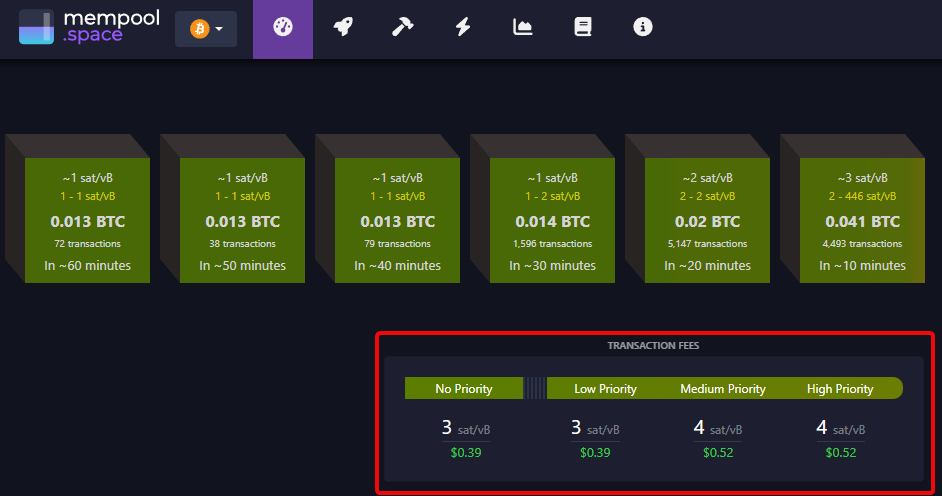
Before sending a transaction, it is recommended to check the mempool using sites such as mempool.space or https://jochen-hoenicke.de/. These mempool explorers help to ensure that the chosen fee is adequate for the current network load.
- If the mempool is empty, use the minimum fee (e.g. 1-3 satoshi per byte).
- If the mempool is overloaded, set a higher fee.
Author's experience:
"If the transaction has not been confirmed for a long time, increase the fee later using the
RBFfunction to speed up confirmation. Make sure thatReplace By Feeis checked in the transaction settings window."
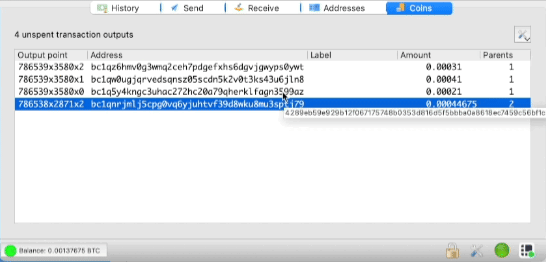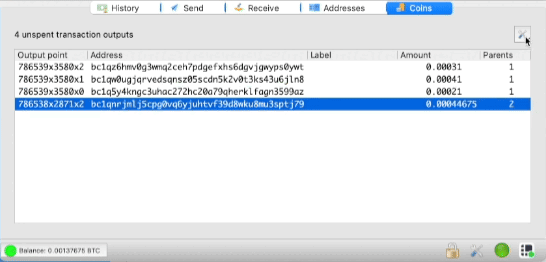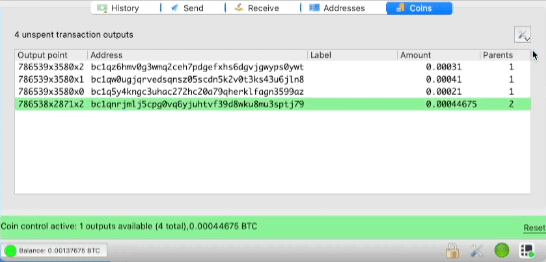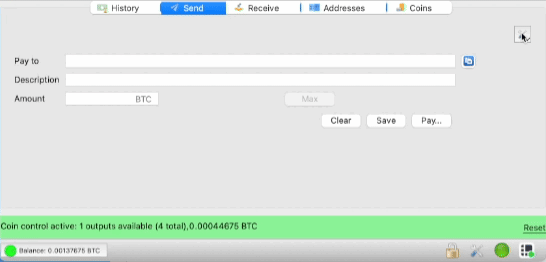
Using the Coin Control Function
To minimize costs, it is recommended to combine small outputs (UTXO) into one transaction. This process is called blockchain payment consolidation.
Consolidation helps reduce fees on future transactions because it reduces the number of inputs needed to create them.
In the view menu, enable the Coins tab. This section allows you to see all UTXO in your wallet.
Press Ctrl and select one or all of the small UTXO strings. Combine them into a single transaction with a minimum fee. It is best to do this during periods of low fees, such as when they are less than 10 satoshi per byte.
Example: If you have 10 outputs of 0.001 BTC, you can combine them into one. This will reduce the size of future transactions and reduce their cost.
To learn all the details, read a separate article about coin control in the Electrum wallet.
Reduce fees by minimizing change
Try to reduce the change in your transaction. This will reduce its overall size.
This allows you to use only those UTXOs that exactly match the amount being transferred, avoiding the need to return the change to another address.
Example: Let's say you have multiple 0.01 BTC outputs and want to send 0.03 BTC. By enabling Coin control, you can select only three 0.01 BTC UTXOs for the transaction. Choose a fee of 10 satoshi per byte for the standard speed and send the transaction. This minimizes both the number of inputs (fewer bytes) and the fee itself.
Summary: How to Avoid Overpaying for Fees
High fees are usually associated with several factors:
- transaction size in bytes,
- large number of UTXOs,
- incorrect choice of commission type,
- using 2FA,
- change,
- network congestion.
To minimize fees:
- Use
Coin controlto select optimal inputs. - Monitor the mempool status via external services.
- Consolidate UTXOs during low fee periods to reduce fees in the future.
- Using new addresses reduces the number of UTXOs in your wallet, which can lower transaction fees.
Connection of addresses with commission size
There are different types of addresses in Electrum. If you are still using outdated Legacy addresses, this may increase your payment fees.
Read a separate guide on Electrum addresses: how and why to create new ones.
In the case of SegWit addresses, the fee is better calculated in satoshis/vbyte, as this is a more accurate unit for calculating fees on the network.
Errors and their solutions
Let's list the main types of errors:
If you see warning the fee for this transaction seems unusually high. This means that one of the points of this article is violated and the cost of the transaction is small in relation to its commission. Reread the article and analyze the reason.
If the reason is network congestion, when miners choose blocks for confirmation with the highest fees, then you need to wait for the load to decrease.
If you see the error Mempool min fee not met – this means that the transaction does not meet the minimum fee to enter the mempool. In this case, it is recommended to create a new transaction with a higher fee. Then send it to your address so that the network accepts it along with the previous transaction.